Why Hydrogen?
A Crucial Storage Medium For The Clean Energy Future
Capable of being stored as a liquid or gas and then burned or converted into electricity (through a fuel cell) – all while producing no greenhouse gas emissions.
Zero Emissions Potential
Abundant Availability
Versatile Application
Quick Refueling Times
High Energy Density
HYDROGEN ADVANTAGES
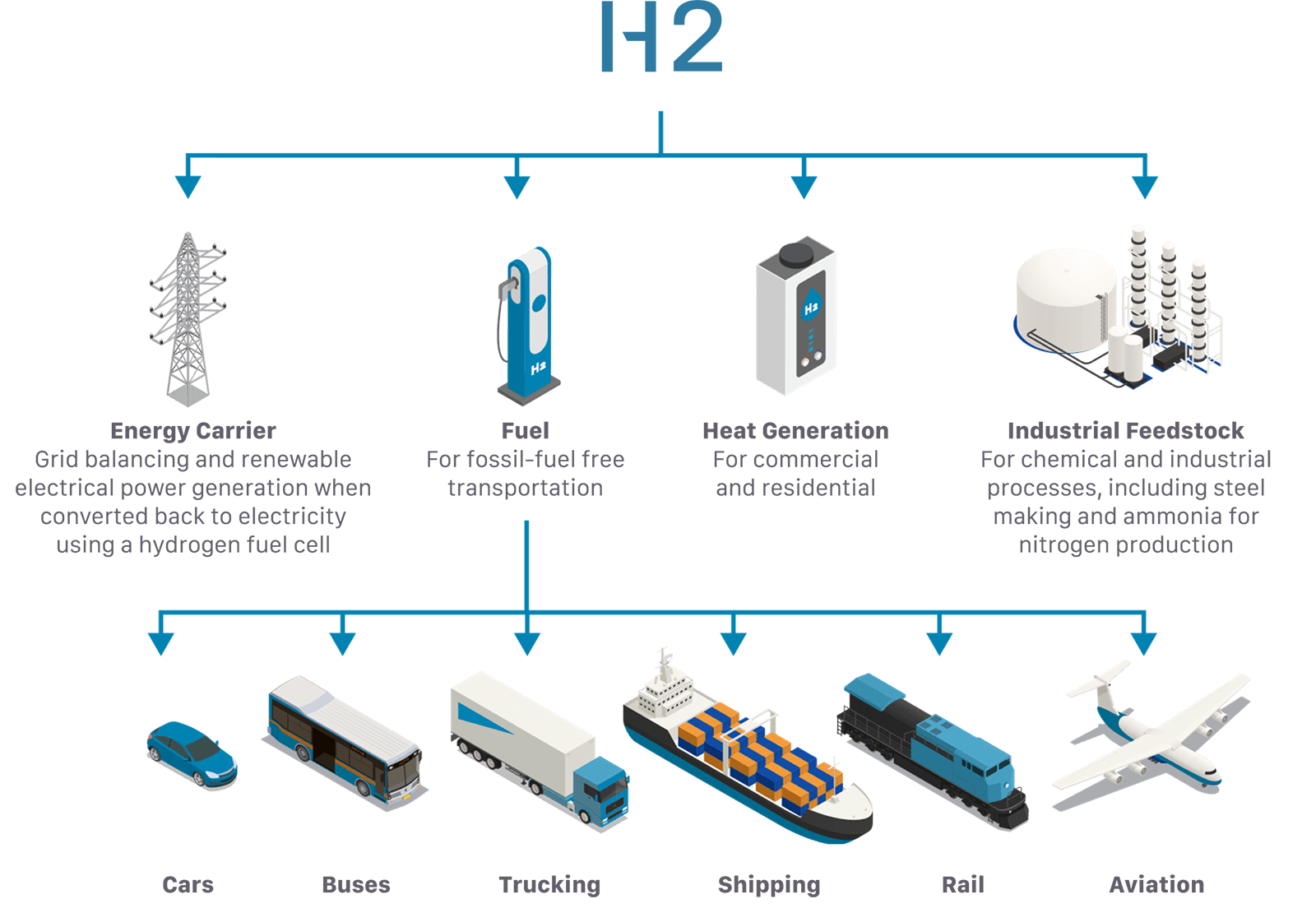
VERSATILITY
Hydrogen can be combined with carbon from CO2 to produce hydrocarbons and virtually any molecule:
- It can be used to produce ammonia, which can be used as feedstock for fertilizers (the majority of current use) or as fuel for new applications such as shipping
- It can also be used to produce methanol, synthetic fuels, or even as a reducing agent to replace coal in iron production


HYDROGEN ADVANTAGES
ENERGY DENSITY
Once it is converted to these commodities, the energy density is increased further, making long-distance transport and long-term storage cost-effective:
- Thus, the conversion to hydrogen derivatives effectively unlocks a global renewable energy trade
- Liquid Ammonia, for example, has almost eight times the energy density (MJ/m3) of lithium-ion batteries and more than 20 times the gravimetric energy density (MJ/kg)1
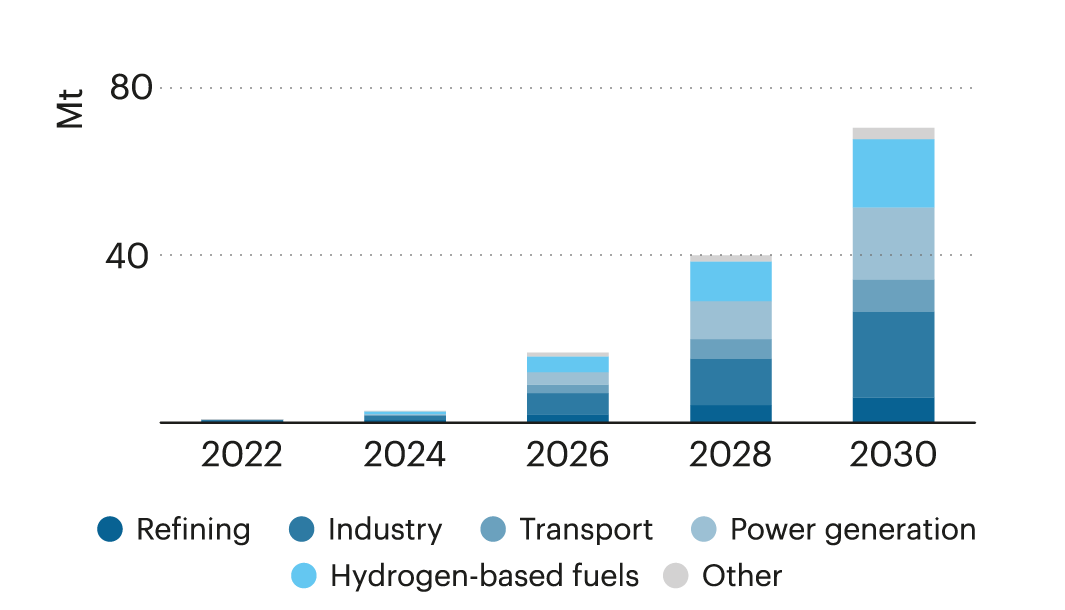
HYDROGEN DEMAND
Hydrogen demand is poised to surge as countries transition towards greener energy solutions, driven by increasing investments in hydrogen fuel technologies and a growing focus on decarbonizing industries and transportation.
Stay Informed
News and Updates